온라인강의
강사명Jeong Hyun Park
강의시간4분
강의개설일2025-12-10
강의소개
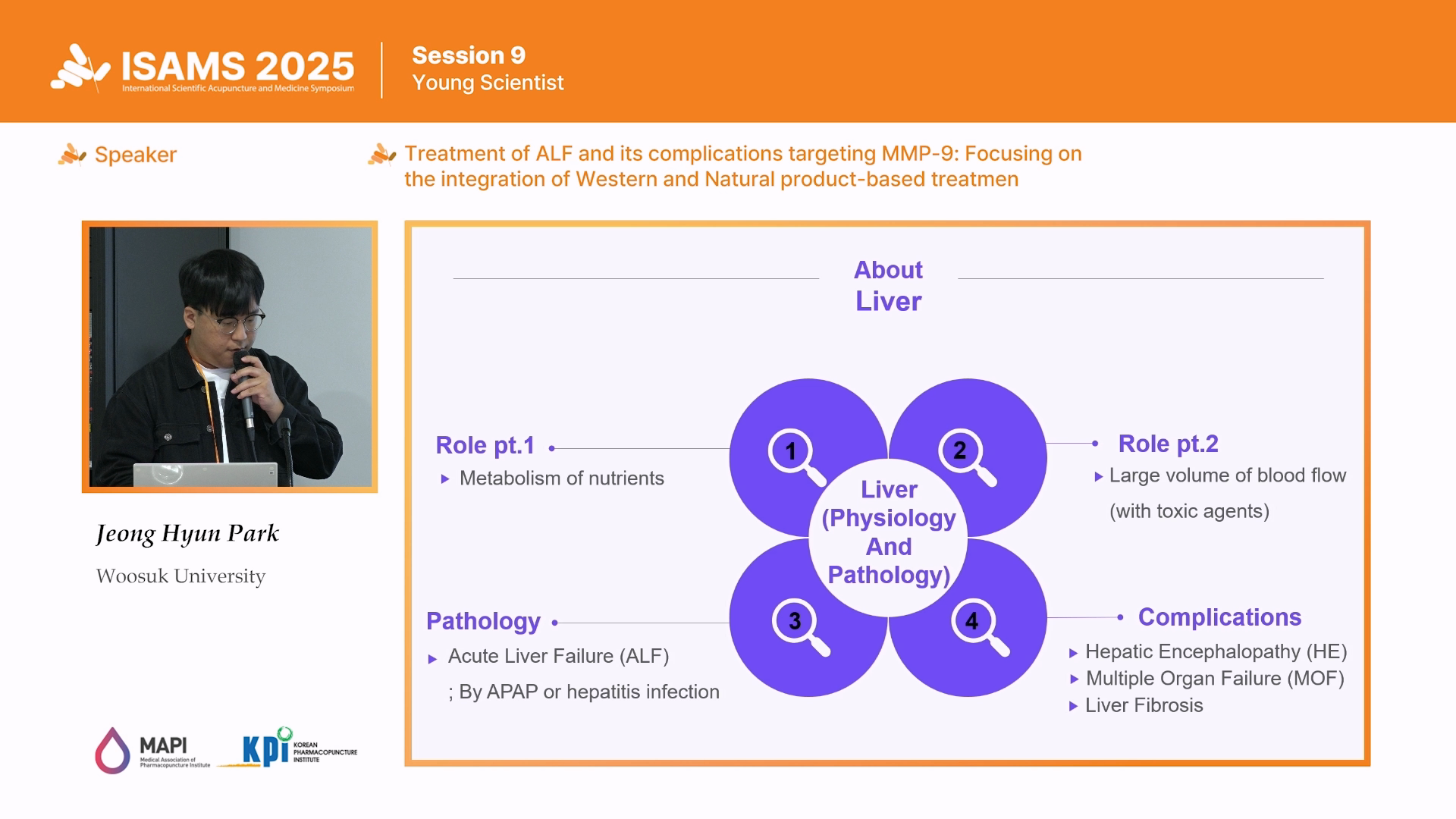
Objectives: Acute Liver Failure (ALF) is a fatal disease characterized by rapid loss of liver function. Recent studies have
highlighted Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a key mediator involved in the pathophysiology of not only ALF
but also various complications, including hepatic encephalopathy (HE), liver fibrosis, and multiple organ failure. This
study aims to illuminate the pathological role of MMP-9 and explore the potential for integrated Western and natural
product-based treatment.
Methods: First, we explored the key pathogenesis of ALF and the induction pathway of MMP-9 in the early stages
of injury. Next, we examined the pathological role of MMP-9 in the major complications that occur during the
progression of ALF. Subsequently, we compared MMP-9 inhibition strategies between Western and natural product
based approaches, analyzing the pros and cons of each approach. Finally, we explored clinical cases of actual fusion
therapy to assess its potential.
Results: Under normal physiological conditions, MMP-9 plays a positive role in regulating hepatocyte regeneration
and neuronal plasticity. However, when pathologically overexpressed during ALF progression, it induces increased
vascular permeability, Extracellular Matrix (ECM) degradation, and Blood-Brain-Barrier (BBB) disruption, which are
closely associated with the development of various complications, including HE, liver fibrosis, and multi-organ failure.
Therefore, MMP-9 was identified as a key factor linking the development of ALF and its complications. In the case
of MMP inhibitors from western treatments, such as GM6001, they can suppress inflammation and liver damage by
directly inhibiting MMP-9, but there is a side effect of worsening liver fibrosis. In the case of natural product extracts
such as beta-asarone, it can induce an anti-inflammatory effect through inhibition of inflammatory cytokines, therefore
reducing MMP-9 expression. However, there is the side effect of relatively low bioavailability and toxicity such as liver
cancer when used in excess.
Conclusion: Both Western and natural product-based monotherapy strategies each have limitations, and some also
raise concerns about adverse effects. Therefore, introducing a Western-Korean fusion treatment from an integrative
medicine perspective has the potential to simultaneously enhance treatment efficacy and safety. However, the specific
mechanism of action and clinical evidence for this fusion treatment strategy are still unexplored, so multidisciplinary
follow-up studies are needed to elucidate them.
강사소개
2019.03.-the present the stuent of Department of Korean Pharmacy, Woosuk
University